A transition edge sensor (TES) is a microcalorimeter based on superconductivity. Compared with alternative technologies like energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS), a TES can provide higher resolution measurements and resolve emission lines at closely adjacent energies. In astrophysics, TES is used to measure the relative abundance of elements like boron, carbon, and oxygen versus silicon […]
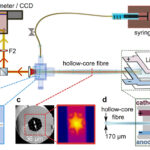
What are the applications for hollow core fiber optical sensors?
Hollow core fiber (HCF) optical sensors are used in applications including Li-ion battery research and development (R&D), robotic arms, civil engineering infrastructural health monitoring, and biosensing. Some of the attributes of HCF optical sensors are small footprints, non-conductance, chemical stability, and high dynamic ranges. In the case of activities like Li-ion R&D, HCFs can be […]
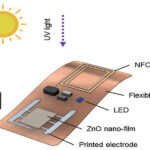
How are zinc oxide (sunscreen) WBG nanomaterials used in sensors?
Zinc oxide (ZnO) is a common ingredient in sunscreen lotions. Less well-known is the fact that it’s also a wide band gap (WBG) semiconductor (3.4 eV). As a nanomaterial, ZnO is being used to develop a wide variety of sensor technologies. Sensor applications for ZnO include health monitoring, chemical sensing, biomedical, and environmental sensors. Some […]
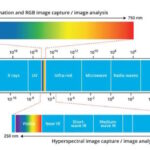
What is hyperspectral imaging?
Hyperspectral imaging is the most comprehensive of the three common image processing technologies. The other two technologies are red-green-blue (RGB) imaging and multispectral imaging. All three are noninvasive and nondestructive and give engineers and scientists different ways to analyze objects. RGB imaging can be quick and inexpensive to implement and provides basic information about an […]
What quantum sensors can be used as GPS replacements?
There’s a variety of quantum sensors available for use as a global positioning system (GPS) replacement including quantum compasses, atomic gyroscopes, and atom interferometers. Several options for a quantum GPS replacement, also called quantum position sensing (QPS), are being developed. Three examples include quantum active navigation that overlays and supplements existing satellite-based GPS systems, quantum […]
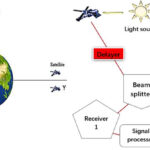
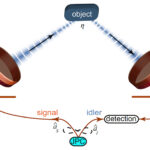
How does a quantum radar sensor work?
It generates quantum entanglement between a microwave resonator and a signal that is emitted toward a target and can theoretically make radar detection up to four times faster in scenarios with comparable signal power and target noise. It also reduces susceptibility to jamming. A microwave quantum radar begins with a stream of entangled visible-frequency photons […]
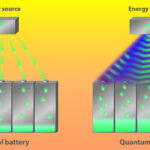
How can quantum sensors and quantum batteries improve electric vehicle operation?
In the near term, quantum sensors are being developed that can more accurately measure EV battery capacity, assess battery safety, and reduce vehicle weight. In the longer term, quantum batteries have been proposed that could dramatically improve the speed and efficiency of battery charging. The energy remaining in an EV battery has been estimated using […]
What are the seven types of quantum sensors?
The seven types of quantum sensors include chemical sensors, clocks, gravimeters, imaging, interferometers, magnetometers, and thermometers. Several types of quantum sensors are already in use, and more are being developed for commercialization. They can be used in a wide variety of applications from earth sciences to molecular biology and wide band gap power semiconductors. Chemical […]
What technologies are used to make quantum sensors?
Quantum sensors rely on quantum mechanical principles like entanglement, interference (also called superposition), discrete quantum states, and coherence. They are unlike quantum computers, which need highly stable environments for operation. Some quantum sensors can operate at room temperature. As a result, quantum computers are still a work in progress, while quantum sensors are used today. […]
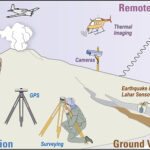
What sensors are used to monitor volcanoes?
Monitoring volcanoes is complex, and it’s an important activity to ensure public safety in many areas of the world. It involves monitoring ground deformations, earthquakes and vibrations, volcanic gas, rock and water chemistry, and remote sensing from satellites. Volcano monitoring needs to be implemented on a continuous basis or in near-real-time and is an extreme […]