Texas Instruments introduced the industry’s most accurate 3D Hall-effect position sensor. With the TMAG5170, engineers can achieve uncalibrated ultra-high precision at speeds up to 20 kSPS for faster and more accurate real-time control in factory automation and motor-drive applications. The sensor also provides integrated functions and diagnostics to maximize design flexibility and system safety, while […]
Hall Effect
Gear tooth speed sensor employs magnetoresistance technology
Allegro MicroSystems, Inc. has introduced a new, state-of-the-art giant magnetoresistance (GMR) speed sensor that measures the rotation of ferromagnetic gears. The ATS19480 speed sensor IC provides a single-channel solution that’s ideal for hybrid and pure electric vehicle transmissions, with use cases extending to two-wheelers, off-road vehicles, and industrial application designs requiring speed-only information. Combining advanced GMR […]
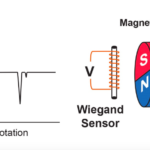
The Wiegand Effect at Work: from lab curiosity to versatile product
What is the Wiegand Effect? Ferromagnetic materials – such as iron, nickel, cobalt, or alloys containing these elements – have a special property: When samples are exposed to an external magnetic field, they become magnetized, creating a magnetic field of their own. Moreover, they remain magnetized when the external field is removed. Ferromagnetic materials vary […]
Hall-effect position sensors incorporate decoupling capacitors
TDK Corporation expands its Micronas 3D HAL sensor portfolio with the Hall-sensor family HAC 39xy*, which features integrated capacitors for stray-field robust position detection in automotive and industrial applications. The TO92UF package was designed explicitly for PCB-less applications, combining both a chip from the HAL 39xy family featuring stray-field compensation capability and up to two […]
Graphene Hall sensor operates at cryogenic temps and optimized for high field measurements
Paragraf introduces the GHS-C Graphene Hall Sensor (GHS), providing the industry’s only viable approach to measuring magnetic field strengths of 7 Tesla (T) and above, at temperature extremes below 3 Kelvin (K). Paragraf has entered volume production of the GHS-C, a Graphene-based Hall sensor optimized to provide high field measurements while operating at cryogenic temperatures. […]
Direct-angle hall-effect sensors get ASIL-B status
TDK Corporation has upgraded its Micronas 3D HAL direct-angle Hall-effect sensor family, HAL 37xy (HAL 37xy, HAR 37xy, and HAC 37xy),* for automotive and industrial applications regarding functional safety aspects. All members of HAL 37xy are now defined as SEooC (Safety Element out of Context) ASIL B-ready, according to ISO 26262. HAL 37xy rotary position […]
Hall effects sensor optimized for low-field environments, normal ambient temps
Paragraf announces a new graphene Hall effect sensor ideally suited to battery applications, such as the electric vehicle (EV) sector. The graphene GHS01AT Hall Effect sensor is optimized for use in relatively low field environments and normal ambient temperatures. Bringing the magnetic field measurement resolution towards that of more complex magnetic sensors, yet with the […]
What application problems do newly released sensors solve?
Coping with the application environment is one of the more complex issues that sensors must address. To survive in harsh environments, sensors manufacturers improve the ruggedness of their sensors in many different ways. Three recently announced products exemplify the differences. For dusty and wet environments, Sensata Technologies ACW4 single turn and TCW4 multi-turn absolute Hall […]
Modular Hall effect sensors are well-sealed, easy-to-install
Sensata Technologies today announced the availability of the new ACW4 Single Turn and TCW4 Multi-Turn Absolute Hall effect sensors, which feature an over-molded, two-part modular construction that provides engineers with exceptional design flexibility. The sensing electronics are encased in a thermoplastic polyamide shell while the separate activating magnet is external to the sensor assembly. This […]
Hall effect magnetic torque sensor boosts EPS drivability for safer, sustainable motoring
TT Electronics has introduced the SX-4462 Hall effect magnetic non-contact torque sensor, a flexible and cost-effective sensor offering high accuracy and diagnostic capabilities for electronic power steering (EPS) applications including off-road vehicles (ORVs), three-wheelers, light commercial trucks, and tractors. The SX-4462 fourth-generation Magnetorque (MT4) is easy to integrate, leveraging TT’s system expertise and development support. Additional […]