Temperature is the most commonly measured physical quantity. Thermometry, the measurement of temperature, involves a wide range of technologies. Its uses range from maintaining a comfortable and safe environment for people to industrial processes operating at over 3,000 °C and quantum computing operating at near absolute zero. This FAQ reviews some of the more common […]
Thermistor
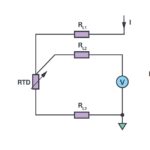
What’s the difference between 2-, 3-, & 4-wire RDT sensing?
The difference is measurement accuracy. Using 2-wire resistance temperature detector (RTD) sensing provides good accuracy (maybe), the accuracy of 3-wire sensing is better, and 4-wire sensing provides the best accuracy. In addition, there’s the option of using Wheatstone bridge topologies to improve the performance of 2- and 3-wire RDTs. This FAQ begins with a review […]
How can printed temperature sensors address a variety of applications?
With printed temperature sensors poised to grow substantially over the next decade, this seems like a very appropriate question. Based on nanostructured silicon composite inks, PST Sensors (of South Africa) thin film printed and flexible temperature sensors are available in a suite of temperature sensing systems. Its silicon nanoparticle negative temperature coefficient (NTC) thermistor can […]
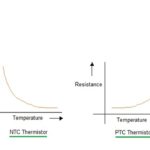
What is the difference between an NTC and a PTC thermistor?
Both negative temperature coefficient (NTC) and positive temperature coefficient (PTC) thermistors’ values change as a result of temperature but impact their use differently. For NTC thermistors, as temperature increases, the resistance drops from high to low and allows current to pass through. In a circuit, they can limit in-rush current by self-heating when current is […]
How can the new temperature-sensitive COVID-19 vaccines’ temperatures be ensured?
The newly developed COVID-19 vaccines require low temperature storage to ensure their efficacy. For the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) specifically states that it should be stored in an ultra-cold freezer, thermal shipping container or refrigerator. The ultra-cold freezer’s temperature should be maintained between -80°C and -60°C (-112°F and […]
How can data loggers help ensure food and beverage safety?
Just about all areas of the food and beverage industry including commercial kitchens, transportation, storage or food service, require temperature and often humidity monitoring to ensure that the product has been kept within an acceptable range to avoid contamination and bacteria growth. The technology requirements are essentially the same for the sensor in each of […]
How can you get digital temperature data?
At Sensors Expo 2018, Mike Mays from Analog Devices explains the LTC2983, a temperature to bits IC. The IC is designed to be extremely easy to use part. Everything necessary to measure temperature is performed by the chip and its output is in direct degrees C. In the display, an “EMI (electromagnetic interference) Hairball from […]
What’s the temperature of this thing?
Of course, there are many follow-up questions regarding where or when such as: on just the surface, in the center, on average, instantaneously, or steady state, to name a few. The standard temperature measurement technique that many people first encountered was the mercury (Hg) thermometer to determine if they had a 98.6° or higher temperature. […]
Interchangeable Thermistors for High-Accuracy Sensing
Interchangeability over a broad temperature range that eliminates the need to individually calibrate or provide circuit compensation for part-to-part variability is a key design attribute for many sensors. For thermistors, that is exactly what Ametherm’s ACCU-Curve NTC thermistors deliver. In addition, the thermistors have long-term stability and reliability for high-accuracy temperature sensing, control and compensation […]
IC Simplifies Digital Temperature Measurements
At Sensors Expo 2016, Mike Mayes, a Design Engineering Section Leader from Linear Technology, demonstrates the capabilities of the LTC2983 temperature-to-bits converter that provides thermistor, thermocouple RTD and diode-based digital temperature measurements. For more information about the LTC2983, click here.