Temperature sensing was the initial COVID-19 detection process to isolate people with a temperature, who may have had the virus, from others. Healthcare facilities including doctor’s offices and other locations frequently used and continue to use non-contact thermal sensing as a precautionary step to prevent the spread of the virus.
In April 2020, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) released “Enforcement Policy for Telethermographic Systems During the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Public Health Emergency Guidance for Industry and Food and Drug Administration Staff” and it has not been revised or updated since that time. Another FDA site, “Thermal Imaging Systems (Infrared Thermographic Systems / Thermal Imaging Cameras)” explains, “thermal imaging systems and non-contact infrared (IR) thermometers (NCITs) use different forms of infrared technology to measure temperature.”
While temperature screening for COVID-19 has been criticized for its effectiveness, many in the private sector have continued to look for an improved technique for non-contact thermal sensing since the public is interested in an accurate detection technique.
Exergen Corporation’s TemporalScanner Thermometer TAT2000-C SmartGlow for Home Use is a totally non-invasive system with advanced IR technology to obtain quick, easy and consistently accurate measurements. They recently announced that it was backed by more than 100 clinical studies and sets milestone for proven accuracy in detecting temperatures. For proper home use, the company recommends twice daily usage for morning and evening fever detection.
Another company, MachineSense FeverWarn system provides self-service thermal scanning and screening. The addition of OPX technology allows the FDA compliant measurement of temperature within 1.5 seconds from a person’s fist, wrist or forearm placed 1-4 inches away under the scanner. Then it provides either a flashing green or red screen with the temperature display.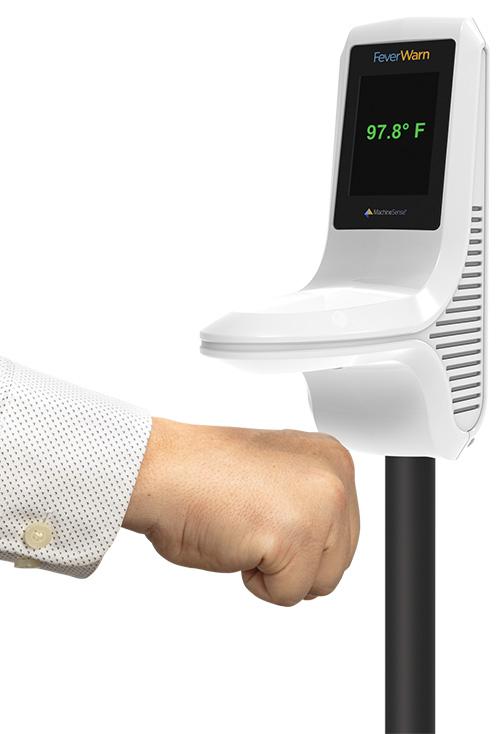
Image courtesy of MachineSense
The company’s OPX technology uses multiple geometric spatial sensors and artificial intelligence (AI)-based algorithms to extend the ambient range of infrared scanners by up to 50% simplifying the physical distance requirement.
Still, the proven means of detecting COVID-19 is through antigen testing.
