The main difference between passive and active radio-frequency identification (RFID) tags is the absence (passive) or presence (active) of an internal power source. Because of these primary differences, there are several secondary differences. Understanding these differences is the key to properly selecting the most appropriate RFID system for a specific application.
Passive RFID
Since they have no internal power source, a standard passive RFID tag consists only of an IC and internal antenna. To operate, the passive RFID tag obtains its energy from the signal transmitted by an RFID reader. After reception at the tag’s antenna, the energy powers the IC which generates a signal back to the RF system. This limited system places restrictions on the capabilities of the passive RFID based on operating frequency.
Low Frequency (LF) (125 – 134 kHz) has an extremely long wavelength with usually a short read range of about 1 – 10 centimeters. This frequency range it is not significantly affected by water or metal.
High Frequency (HF) & Near-Field Communication (NFC) (13.56 MHz) is a medium wavelength with a typical read range of about 1 centimeter up to 1 meter.
Ultra High Frequency (UHF) (865 – 960 MHz) is short, high-energy wavelength of about a one meter which provides a long read range. While they can be read from an average distance of about 5 – 6 meters, larger UHF tags can achieve up to 30+ meters of read range.
Because of their lower price point per tag, passive RFID tags are used for applications such as access control, file tracking, race timing, supply chain management, smart labels and more.
Active RFID
With an internal battery as their power source, active RFID systems have three essential parts: a reader or interrogator, antenna, and a tag. The battery enables these RFIDs to have extremely long read ranges and large memory banks. The two main frequencies used by active systems are 433 MHz and 2.45 GHz. The longer wavelength of RFID systems that operate on the 433 MHz enables them to work a little better with non-RF friendly materials like metal and water.
There are two different types of active RFID tags: transponders and beacons.
In a system with an active transponder tag, similar to a passive system, the reader initially sends a signal, and then the active transponder replies by sending a signal back with the appropriate data. Transponder tags are very efficient and conserve battery life when the tag is out of range of the reader.
In a system that uses an active beacon tag, the tag will beacon or send out its specific information every 3 – 5 seconds. While active tag’s beacons can be read hundreds of meters away, to conserve battery life, their transmit power can be reduced to reach around 100 meters read range.
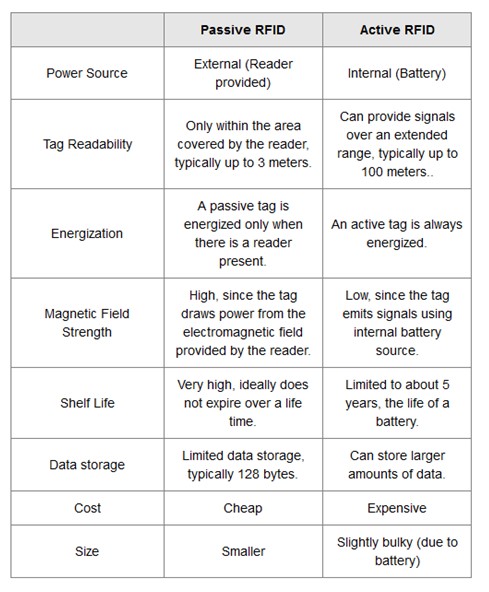
Active RFID systems are usually used in the oil and gas industry, shipping and logistics, construction, mining and high-value manufacturing. Table 1 provides a quick summary of the differences that may impact the choice of passive vs active RFID.
Table 1. Summary of key differences between passive and active RFID tags. Source: Difference Between Active And Passive RFID Tag Systems (tutorialsweb.com)
References
Active RFID vs. Passive RFID: What’s the Difference? – atlasRFIDstore
Difference Between Active And Passive RFID Tag Systems (tutorialsweb.com)