Buoys were historically employed as simple mechanical structures to identify a safe navigation route or mark hazards such as reefs and below the surface rocks. The addition of battery and lights brought an electrical aspect to them and increased their visibility at night. These days a buoy can be part of the Internet of Things (IoT) with a variety of sensors, data logging, networking, communication and power gear.
The goal of the United Kingdom (UK) Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC) EPSRC USMART project that ran from May 2017 until Jan 2021 was to create a smart underwater sensing framework based on ultra-low-cost underwater communication and sensing devices (‘smart dust’). The buoys in this project received data from underwater sensors and subsea assets that were transmitted acoustically because underwater radio wave propagation is severely limited. The data was then transmitted to a terrestrial base station. One of the data collection nodes was actually a multi-sensing platform that had nine exteroceptive sensors: temperature, pressure, humidity, optical, distance, sound, magnetic field, accelerometer and gyroscope.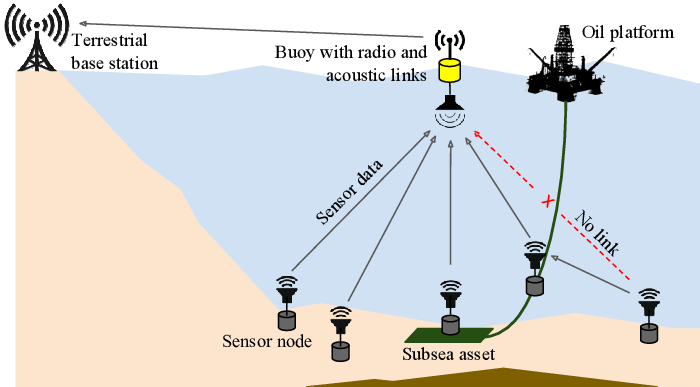
While USMART was a project to resolve issues in underwater sensing and communications, some suppliers already offer a variety of sensors and associated electronics on commercially available buoys. For example, NexSens Technology, a company specializing in the design and manufacture of real-time environmental measurement systems, offers monitoring systems for different water-based environments. For dredging operations, the company’s CB-450 data buoy has sensors for dredge turbidity monitoring, temperature profiling, dissolved oxygen monitoring, limnology research and weather monitoring on inland lakes. Other sensors that can be added to this or other buoys include water quality, water level, velocity currents and waves, weather solar and soil sensors. Incorporating solar panels to power the sensors and electronics, the buoys have data loggers to capture the sensor data prior to transmitting it using cellular telemetry.
