by Charles Pao, senior marketing specialist, CEVA Motion sensing devices are all around us and in several of the electronics that we use daily. Motion sensors are in earbuds – noticing taps to change songs or pausing music when we take them out of our ears. They’re used for head tracking in virtual reality (VR) […]
FAQ
Creating unique devices with haptic touch technology
By Nedko Ivanov, Aito Consumer technology products are becoming increasingly difficult for designers and manufacturers to differentiate. Laptops, in particular, are all of a similar size and shape and offer the same functionality. Clamshell laptops typically combine the same three features – a display, a keyboard, and a touchpad – with few aspects that distinguish […]
What are different types of biometric sensors?
The term “Biometrics” is derived from “bio’” which means life, and “metrics”, which means measurement. Biometrics is developing for use in various technologies, including the unique identification and recognition of people. The technology at its current juncture is widely used in security and surveillance systems. Biometrics also has the possibility of converging with other technologies […]
The automotive Tire Pressure Monitoring System, Part 4: Issues
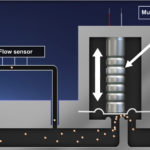
Sensor-based monitoring systems for tire pressure can warn of potential problems, but there’s much more to the story than just a pressure-measurement system. The TPMS adds a highly specific safety-related feature to cars. However, as with many presumably good ideas, the “devil is in the details”, and that’s especially true for the TPMS. There are […]
The automotive Tire Pressure Monitoring System, Part 3: implementation
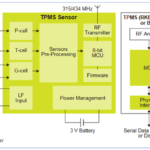
Sensor-based monitoring systems for tire pressure can warn of potential problems, but there’s much more to the story than just a pressure-measurement system. Once the decision was made to use the direct measurement technique, IC vendors developed the needed components and equally important packaging. A TMPS requires a significant amount of analog, digital, and RF […]
The automotive Tire Pressure Monitoring System, Part 2: perspectives
Sensor-based monitoring systems for tire pressure can warn of potential problems, but there’s much more to the story than just a pressure measurement system. During the comments phase before the formal safety mandate was published per the legislative direction, the automotive-related communities had differing views on the need or wisdom of the electronic TPMS: The […]
The automotive Tire Pressure Monitoring System, Part 1: the situation
Sensor-based monitoring systems for tire pressure can warn of potential problems, but there’s much more to the story than just a pressure-measurement system. You may have had the misfortune to have the “Check Engine” light come on in your car. This single illuminated indicator encompasses a wide range of possible problems ranging from trivial where […]
Principles, selection and design with piezoelectric actuators
By Patrik Kalbermatten, Senior Manager – Distribution Promotion Product Management Magnetic, Sensor & Actuator at KEMET Electronics Corporation a YAGEO company Piezoelectric actuators that exploit the inverse piezoelectric effect to produce a displacement in response to an applied voltage can offer an alternative to familiar electromagnetic devices such as motors and solenoids. They offer advantages […]
What are capacitive pressure sensors?
When automotive ignition and carburetor systems initially required inputs from the engine to control spark and fuel and lower vehicle emissions, a capacitive pressure sensor was designed to specifically measure manifold absolute pressure (MAP) and barometric absolute pressure (BAP). Called a silicon capacitive absolute pressure (SCAP) sensor, it consisted of a micromachined diaphragm etched into […]
What is the role of sensor fusion in robotics?
As robots become increasingly autonomous, sensor fusion is growing in importance. Sensor fusion merges data from multiple sensors on and off the robot to reduce uncertainty as a robot navigates or performs specific tasks. It brings multiple benefits to autonomous robots: increased accuracy, reliability, and fault tolerance of sensor inputs; extended spatial and temporal coverage […]